Russia Closing its Gas Supply to Europe
April 28, 2022 2022-04-28 18:35Russia Closing its Gas Supply to Europe
Russia Closing its Gas Supply to Europe
Risks that arise/will arise from Russia closing its Gas supply to Europe
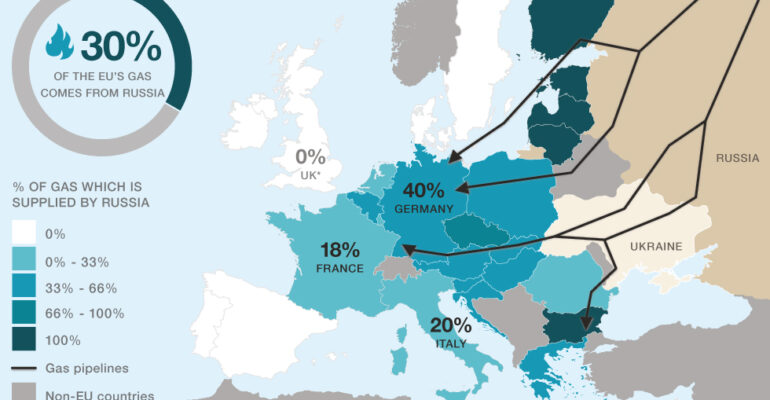
There are multiple risks the European Continent, particularly the members of the European Union (EU), is facing. Oil is universally considered one of the essential resources in modern economies. The significant risks from rising oil prices include the risk associated with the rise of commodity and household prices that would limit the purchasing power of consumers. Another risk is the increasing cost of business, which will negatively affect profit margin, especially for small and medium enterprises as it could be passed down to consumers if not enough Government subsidy will be deployed. Lastly, the risk of mass unemployment due to rising costs could further burden European economies, especially if transportation costs continue to increase.
How it can affect Europe’s Market
On a macro level, exports of European countries could be much more expensive than importing countries worldwide. This could cause an increase in export prices that the importing countries would have to bear or worse; these importing countries will start to look for alternative markets to import from, causing a loss of revenue for Europe’s economies. Second, European countries could opt to shoulder the additional costs rather than pass them down to importing countries; this would cause reduced profit margin and lower overall revenue.
How it can increase Inflation
Historically, the rise of oil prices has led to inflation. In economics, this is called a “Cost-Push Inflation,” which means that the leading inflationary cause is the increase in the cost of production. It is a lose-lose economic scenario since inflation is not driven by increased demand or a decrease in supply. In this case, almost all of a country’s stakeholders (its population, businesses, and government institutions) would have to bear this.
Can it cause a recession in Europe due to higher prices, conflict of war, and the banning of Russian commodities?
It may cause a recession if European economies do not 1) find a decent alternative to Russian oil, 2) the conflict spillover to other European countries and 3) if the West will employ continued sanctions. However, the economies that would mainly be facing this predicament would be the countries highly reliant on Russian oil and/or economies that export a considerable chunk of their products and services to Russia.
US Natural Gas ETF (UNG)
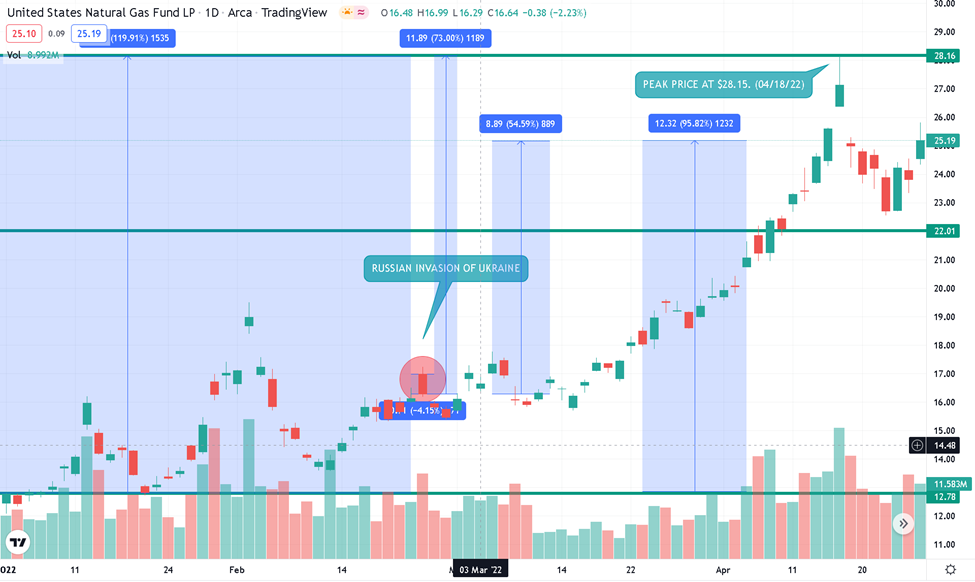
Above is the 2022 chart of UNG, wherein we will examine the timeline from the beginning of 2022 to paint a complete picture of all major events that have taken place so far. The 3rd of January, the first trading day, saw a close of $12.77. Before the Russian Invasion of Ukraine on the 23rd of February, it closed at P16.12. A 26% increase from its first trading day. Following the formal announcement of a “Special Military Operation” in Ukraine, UNG closed at $16.29. A 4% drop from its market open price of $16.98. However, UNG started to rally by March, when the EU first considered the US a possible natural gas source. It ultimately reached as high as $28.15 by the 18th of April. A staggering almost 120% increase from its year-to-date price and around 73% increase from the announcement of Russia’s infamous “Special Military Operation” in Ukraine. Yesterday, the 27th of April, the market closed at $25.19, translating to around a 95% increase year-to-date. It was also about a 54% increase from the start of the invasion of Ukraine on the 24th of February.